Developmental
Diseases
Intellectual disabilities
Intellectual disabilities (ID) are neurodevelopmental disorders characterized by impaired intellectual functioning affecting learning, reasoning, and problem-solving skills, as well as deficits in adaptive behavior, impairing social and practical daily skills. ID is usually associated with autism spectrum disorders. ID affects 2-3% of the population and is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous disease. The genes involved in ID are very diverse and participate in multiple cellular processes and embryonic development.
Our team is interested in diagnosing and understanding the molecular causes of syndromic IDs and in particular the following syndromes :
Mowat-Wilson syndrome (MWS, MIM # 235730) is characterized by microcephaly, epilepsy, cerebral malformations of the agenesis of the corpus callosum, Hirschsprung’s disease (or congenital megacolon), cardiac and renal anomalies. MWS is caused by de novo monoallelic mutations in ZEB2 encoding an essential transcription factor during embryonic development. Most of the mutations identified in MWS are truncating mutations or deletions responsible for a haploinsufficiency of ZEB2. We have shown that some missense mutations located in the C-terminal zinc finger domain of ZEB2 are responsible for a milder disease phenotype1.
Goldberg-Shprintzen syndrome (GOSHS, MIM # 609460) combines severe ID, microcephaly, brain and heart abnormalities, and Hirschsprung’s disease. GOSHS is caused by biallelic mutations in KIAA1279 aka KIFBP (KIF1-binding protein) encoding a cytoplasmic protein that interacts with the cytoskeleton2.
Pitt-Hopkins syndrome (PTHS, MIM # 610954) is characterized by severe ID, behavioral problems, and hyperventilation. PTHS is due to de novo monoallelic mutations in TCF4 encoding a transcription factor of the E-protein family. We described the diagnostic criteria for typical PTHS3, showed that it is important to evoke this diagnosis in some cases of moderate ID4 , and contributed to recommendations for the management of this disease5.
The CSDE1 gene (Cold Shock Domain-containing E1-alias UNR: Upstream of NRAS, MIM # 191510) has been implicated more recently in ID associated with autistic disorders. CSDE1 encodes a protein that regulates translation and mRNA stability and has been implicated in many biological processes such as cell migration and cycle, apoptosis, embryonic development, neurogenesis and neuronal differentiation. By studying a patient with a monoallelic mutation of CSDE1 responsible for haploinsufficiency, we clarified the clinical phenotype of this condition and showed the role of this factor in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and in cell adhesion6 (Figure 1).
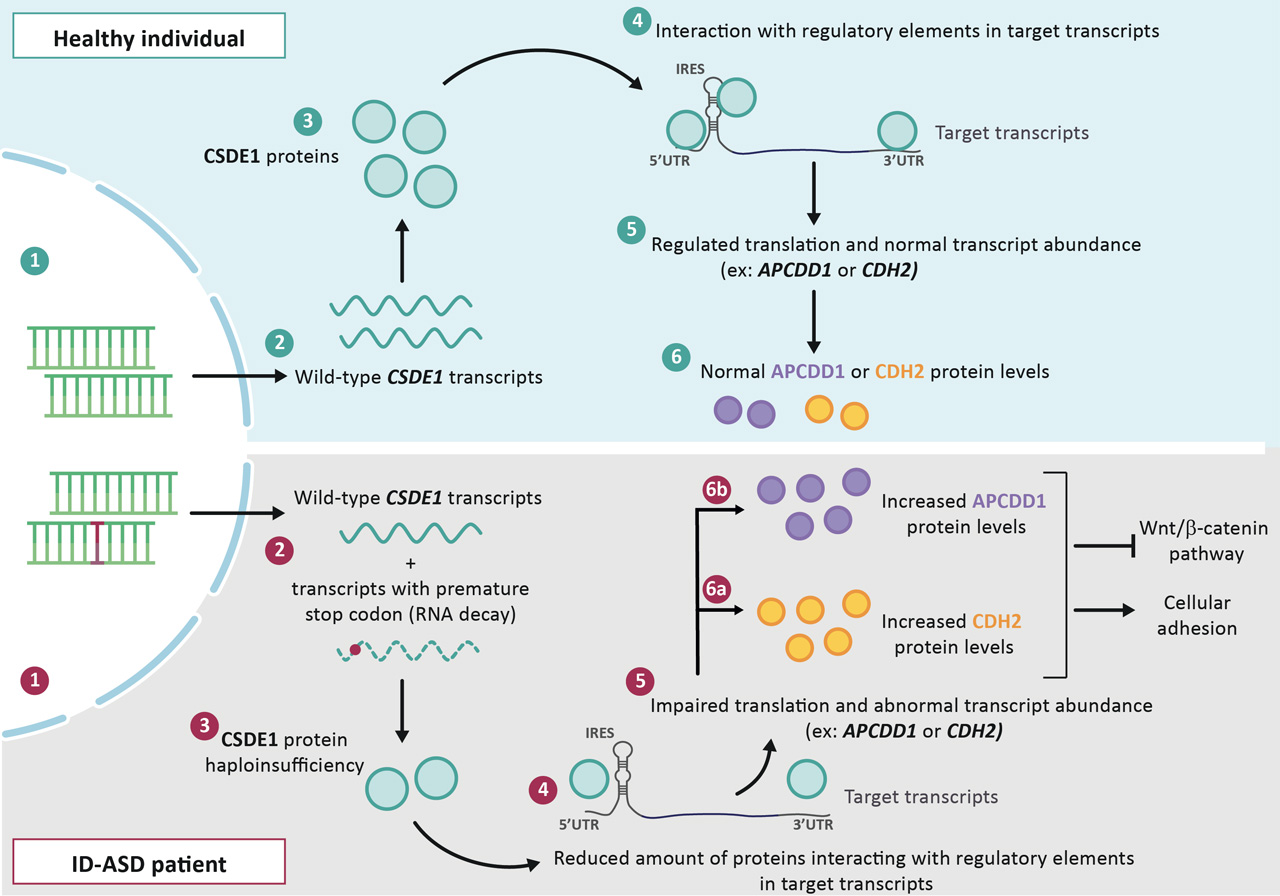
Figure 1. Pathophysiological model of the CSDE1-haploinsufficiencyrelated disease6.
References
- Ghoumid, J, Drevillon, L, Alavi-Naini, SM, Bondurand, N, Rio, M, Briand-Suleau, A et al.. ZEB2 zinc-finger missense mutations lead to hypomorphic alleles and a mild Mowat-Wilson syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22 (13):2652-61. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt114. PubMed PMID:23466526 .
- Drévillon, L, Megarbane, A, Demeer, B, Matar, C, Benit, P, Briand-Suleau, A et al.. KBP-cytoskeleton interactions underlie developmental anomalies in Goldberg-Shprintzen syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22 (12):2387-99. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt083. PubMed PMID:23427148 .
- Whalen, S, Héron, D, Gaillon, T, Moldovan, O, Rossi, M, Devillard, F et al.. Novel comprehensive diagnostic strategy in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome: clinical score and further delineation of the TCF4 mutational spectrum. Hum Mutat. 2012;33 (1):64-72. doi: 10.1002/humu.21639. PubMed PMID:22045651 .
- Mary, L, Piton, A, Schaefer, E, Mattioli, F, Nourisson, E, Feger, C et al.. Disease-causing variants in TCF4 are a frequent cause of intellectual disability: lessons from large-scale sequencing approaches in diagnosis. Eur J Hum Genet. 2018;26 (7):996-1006. doi: 10.1038/s41431-018-0096-4. PubMed PMID:29695756 PubMed Central PMC6018712.
- Zollino, M, Zweier, C, Van Balkom, ID, Sweetser, DA, Alaimo, J, Bijlsma, EK et al.. Diagnosis and management in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome: First international consensus statement. Clin Genet. 2019;95 (4):462-478. doi: 10.1111/cge.13506. PubMed PMID:30677142 .
- El Khouri, E, Ghoumid, J, Haye, D, Giuliano, F, Drevillon, L, Briand-Suleau, A et al.. Wnt/β-catenin pathway and cell adhesion deregulation in CSDE1-related intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2021; :. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01072-7. PubMed PMID:33867523 .
